CMMC 2.0 – Strategic Direction & Clarity of Program

On November 4, 2021, the Department of Defense (DoD) introduced the enhanced Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) 2.0 program, marking the completion of an internal assessment of the program by senior DoD officials.
Safeguarding sensitive information continues to be the strategic direction of the CMMC program given the increasingly frequent and complex cyberattacks targeting the Defense Industrial Base (DIB).
Evolution of CMMC 2.0
The DoD launched an internal review of CMMC’s implementation in March 2021. This involved engaging cybersecurity and acquisition leaders within the Department for a comprehensive and programmatic assessment to refine policy and implementation of the program.
In announcing CMMC 2.0 in November 2021, the DoD indicated their internal review had achieved its primary goals for an updated program structure and requirements. These goals included:
- Safeguard sensitive information to enable and protect the warfighter
- Dynamically enhance DIB cybersecurity to meet evolving threats
- Ensure accountability while minimizing barriers to compliance with DoD requirements
- Contribute towards instilling a collaborative culture of cybersecurity and cyber resilience
- Maintain public trust through high professional and ethical standards
"CMMC 2.0 will dramatically improve the cybersecurity of the DIB. By establishing a more collaborative relationship with industry, these updates will support businesses in adopting the practices they need to thwart cyber threats while minimizing barriers to compliance with DoD requirements.”
Jesse Salazar, Deputy Assistant Secretary of Defense for Industrial Policy
Key Features of CMMC 2.0
There are several changes with the implementation of CMMC 2.0 that cultivate and refine the program’s original requirements. These enhancements include:
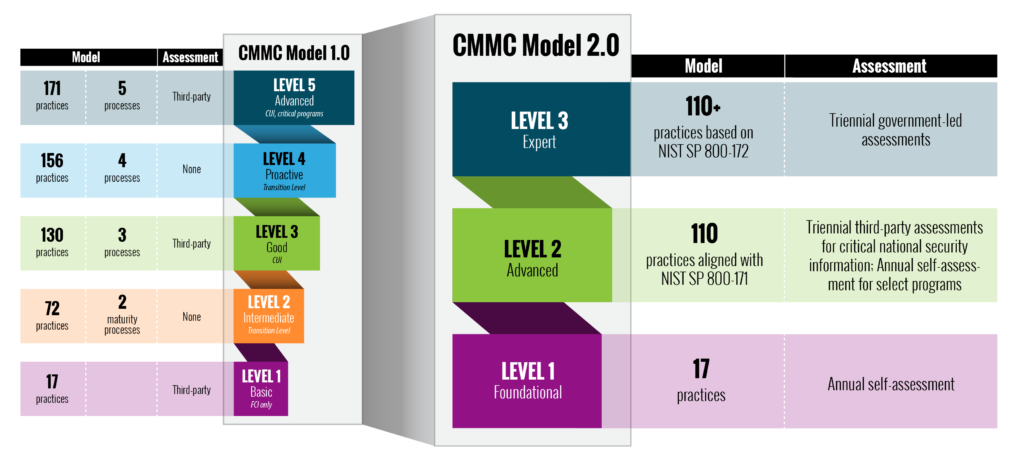
Streamlined Model
- Reduce the model from five to three compliance levels to focus on the most important requirements
- Use the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) cybersecurity standards to align with more widely accepted standards
Reliable Assessments
- Allow all companies at Level 1 (Foundational), and a subset of companies at Level 2 (Advanced) to demonstrate compliance through self-assessments to lower costs
- Increase oversight of professional and ethical standards of third-party assessors for greater accountability
Flexible Implementation
- Enable companies, under certain limited circumstances, to make Plans of Action & Milestones (POA&Ms) to achieve certification for broader collaboration
- Allow waivers to CMMC requirements under certain limited circumstances for added flexibility and speed
Implementation Overview of CMMC 2.0
As part of CMMC 2.0 implementation, the required CMMC level will be specified for contractors and subcontractors in the solicitation and Requests for Information (RFI).
Plan of Action & Milestones (POA&M)
The DoD will allow companies to receive contract awards with a POA&M in place to complete CMMC requirements. The intent is to specify a baseline number of requirements to be achieved prior to contract award, to allow a remaining subset to be addressed in a POA&M within a clearly defined timeline. The DoD will also specify a small subset of requirements that cannot be on a POA&M in support of achieving a CMMC certification.
Waivers
The DoD intends to allow a limited waiver process under CMMC 2.0 to exclude CMMC requirements from acquisitions for select mission-critical requirements. Requests for waivers will require approval from senior Defense Department officials and will have a limited duration. The specifics of the waiver requirements will be implemented as part of the rulemaking process.
Rulemaking for CMMC 2.0
The DoD will implement the changes reflected in CMMC 2.0 through the rulemaking process. Once the forthcoming rules go into effect, companies will be required to comply. Rulemaking will be pursued in Part 32 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) and in Part 48 of the Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation Supplement (DFARS) of the CFR. There will be a public comment period seeking stakeholder input to help meet the objectives of the CMMC program as it moves towards full implementation.
The Defense Department intends to suspend the current CMMC Piloting efforts during the rulemaking process and will not approve a CMMC requirement in any DoD solicitation.
Contractors are encouraged to continue to enhance their cybersecurity posture while the rulemaking process is underway. The DoD’s Project Spectrum was developed to help DIB companies assess their cyber readiness and begin adopting stringent cybersecurity practices.
The DoD is exploring opportunities to provide incentives for contractors who voluntarily obtain a CMMC certification in the interim period. Additional information will be provided as it becomes available.
To learn more about CMMC 2.0 and its impact on your business, contact CONNSTEP for additional information.
Information in this article obtained from the Office of the Under Secretary of Defense, Acquisition & Sustainment.
